Función de los aditivos zootécnicos en la productividad y salud de los conejos
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
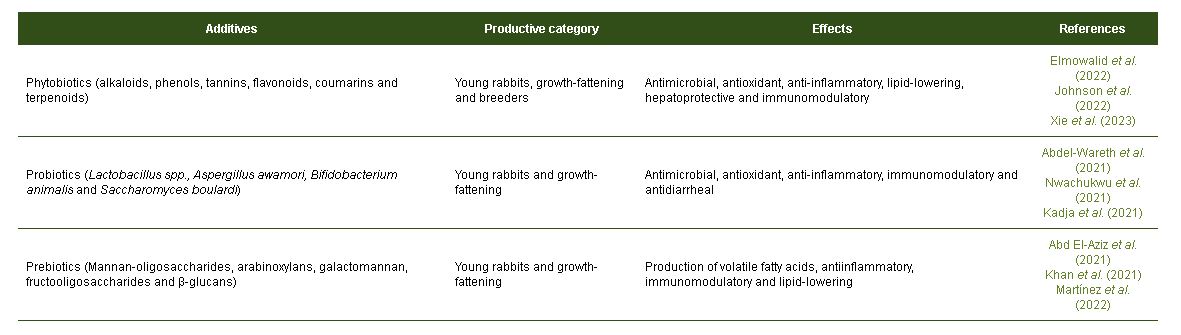
En Latinoamérica, los antibióticos subterapéuticos se utilizan comúnmente en la producción de animales monogástricos, aunque su uso en conejos tiene menor relevancia que en aves y cerdos. Es conocido que su utilización genera resistencia bacteriana y tienen efectos nocivos comprobados en la salud humana. Esta revisión aborda la caracterización y uso de nuevos aditivos nutracéuticos, con énfasis en los fitobióticos, probióticos y prebióticos y su efecto en los indicadores biológicos de conejos en diferentes categorías productivas. Estas alternativas naturales tienen efectos antimicrobianos, antiinflamatorios, antioxidantes, inmunomoduladores e hipocolesterolémicos, lo que puede estimular la microbiota nativa, la producción de ácidos grasos de cadena corta y puede provocar eubiosis microbiana y, por ende, mejorar la salud intestinal, digestibilidad, eficiencia productiva y calidad de la carne de conejos. Además, pueden paliar los efectos perjudiciales de algunas enfermedades bacterianas e intoxicaciones comunes. No obstante, la eficacia de estas alternativas naturales dependerá de la cepa probiótica utilizada, de los metabolitos secundarios mayoritarios en los fitobióticos y de la estructura química de los prebióticos, así como del estado de salud, dieta, edad y categoría productiva de los conejos.
Detalles del artículo

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
- Los autores/as conservarán sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación esta revista. Bajo esta licencia el autor será libre de:
- Compartir — copiar y redistribuir el material en cualquier medio o formato
- Adaptar — remezclar, transformar y crear a partir del material
- El licenciador no puede revocar estas libertades mientras cumpla con los términos de la licencia
Bajo las siguientes condiciones:
- Reconocimiento — Debe reconocer adecuadamente la autoría, proporcionar un enlace a la licencia e indicar si se han realizado cambios. Puede hacerlo de cualquier manera razonable, pero no de una manera que sugiera que tiene el apoyo del licenciador o lo recibe por el uso que hace.
- NoComercial — No puede utilizar el material para una finalidad comercial.
- No hay restricciones adicionales — No puede aplicar términos legales o medidas tecnológicas que legalmente restrinjan realizar aquello que la licencia permite.
- Los autores/as podrán adoptar otros acuerdos de licencia no exclusiva de distribución de la versión de la obra publicada (p. ej.: depositarla en un archivo telemático institucional o publicarla en un volumen monográfico) siempre que se indique la publicación inicial en esta revista.
- Se permite y recomienda a los autores/as difundir su obra a través de Internet (p. ej.: en archivos telemáticos institucionales o en su página web) antes y durante el proceso de envío, lo cual puede producir intercambios interesantes y aumentar las citas de la obra publicada. (Véase El efecto del acceso abierto).
Citas
Abd El-Aziz, A.H., Mahrose, K.M., El-Kasrawy, N.I. & Alsenosy, A.E.W.A. 2021. Yeast as growth promoter in two breeds of growing rabbits with special reference to its economic implications. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências, 93: e20190274, ISSN: 1678-2690. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765202120190274.
Abd El-Hamid, M.I., Ibrahim, D., Hamed, R.I., Nossieur, H.H., Elbanna, M.H., Baz, H. & Awad, N.F. 2022. Modulatory impacts of multi-strain probiotics on rabbits’ growth, nutrient transporters, tight junctions and immune system to fight against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Animals, 12(16): 2082, ISSN: 2076-2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12162082.
Abdel-Azeem, A.A.S. & El-Kader, I.A.A. 2022. Growth performance, carcass attributes, blood hematology and biochemical constituents of growing rabbits supplemented with cinnamon and clove powder. Animal Science Papers & Reports, 40(3), ISSN: 2300-8342. https://www.igbzpan.pl/uploaded/FSiBundleContentBlockBundleModelTranslatableFilesElement/filePath/2207/str351-370.pdf.
Abdel-Wareth, A.A., Elkhateeb, F.S., Ismail, Z.S., Ghazalah, A.A. & Lohakare, J. 2021. Combined effects of fenugreek seeds and probiotics on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, carcass criteria, and serum hormones in growing rabbits. Livestock Science, 251: 104616, ISSN: 1878-0490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2021.104616.
Abdel-Wareth, A.A. & Metwally, A.E. 2020. Productive and physiological response of male rabbits to dietary supplementation with thyme essential oil. Animals, 10(10): 1844, ISSN: 2076-2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10101844.
Abo El-Maaty, H., Aziz, H.A., Dorra, T.M., El Moghazy, G.M. & Eid, R.H. 2019. Replacement of dietary yellow corn by wheat bran with or without multi-enzymes or prebiotic supplementation on nutrient digestibility and blood parameters in growing rabbits. Egyptian Journal of Nutrition and Feeds, 22(2): 359-373, ISSN: 1110-6360. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejnf.2019.79430.
Adli, D.N., Sjofjan, O., Sholikin, M.M., Hidayat, C., Utama, D.T., Jayanegara, A. & Puspita, P.S. 2023. The effects of lactic acid bacteria and yeast as probiotics on the performance, blood parameters, nutrient digestibility, and carcase quality of rabbits: a meta-analysis. Italian Journal of Animal Science, 22(1): 157-168, ISSN: 1828-051X. https://doi.org/10.1080/1828051X.2023.2172467.
Akinpelu, D.A. 2021. Antimicrobial activity of Anacardium occidentale bark. Fitoterapia, 72: 286–287, ISSN: 1873-6971. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0367-326X(00)00310-5.
Ayala, L., Nicola, S., Zoccarato, I., Caro, Y. & Gómez, S. 2012. Salvia spp. como aditivo promotor de crecimiento en dietas de conejos destetados. Revista Unellez de Ciencia y Tecnología, 30: 61-63, ISSN: 1012-7054. http://app.vpa.unellez.edu.ve/revistas/index.php/rucyt/article/view/270/294.
Ayala, L., Silvana, N., Zocarrato, I. & Gómez, S. 2011. Utilización del orégano vulgar (Origanum vulgare) como fitobiótico en conejos de ceba. Revista Cubana de Ciencia Agrícola, 45(2): 159-161, ISSN: 2079-3480. https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/1930/193022245011.pdf.
Ayyat, M.S., Al-Sagheer, A.A., Abd El-Latif, K.M. & Khalil, B.A. 2018. Organic selenium, probiotics, and prebiotics effects on growth, blood biochemistry, and carcass traits of growing rabbits during summer and winter seasons. Biological Trace Element Research, 186: 162-173, ISSN: 1559-0720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1293-2.
Bosscher, D., Van Loo, J. & Franck, A. 2006. Inulin and oligofructose as prebiotics in the prevention of intestinal infections and diseases. Nutrition Research Reviews, 19(2): 216-226, ISSN: 1475-2700. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954422407249686.
Chandra, S., Saklani, S., Kumar, P., Kim, B. & Coutinho, H.D. 2022. Nutraceuticals: Pharmacologically active potent dietary supplements. BioMed Research International, 2022(1): 2051017, ISSN: 2314-6141. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2051017.
Chouegouong, M.T., Majoumouo, M.S., Menkem, E.Z.O., Yimgang, L.V., Toghueo, R.M.K., Etchu, K.A. & Boyom, F.F. 2021. Ethnopharmacological survey and antibacterial activity of medicinal plant extracts used against bacterial enteritis in rabbits. Advances in Traditional Medicine, 1-11, ISSN: 2662-4060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-021-00615-1.
Colitti, M., Stefanon, B., Gabai, G., Gelain, M.E. & Bonsembiante, F. 2019. Oxidative stress and nutraceuticals in the modulation of the immune function: current knowledge in animals of veterinary interest. Antioxidants, 8(1): 28, ISSN: 2076-3921. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8010028.
Dalle-Zotte, A., Celia, C. & Szendrő, Z. 2016. Herbs and spices inclusion as feedstuff or additive in growing rabbit diets and as additive in rabbit meat: A review. Livestock Science, 189: 82-90, ISSN: 1878-0490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2016.04.024.
Diaz-Fuentes, K., Jerez-Collazo, L.R., López-Valoy, B. & Benítez-González, H.R. 2022. Efectos de un bioproducto con microorganismos eficientes como aditivo alimentario en conejos en ceba. Revista CIGET, 1(2): 28-38, ISSN: 1027-2127. https://www.redalyc.org/journal/1813/181373019011/html/.
Dumont, B., Puillet, L., Martin, G., Savietto, D., Aubin, J., Ingrand, S. & Thomas, M. 2020. Incorporating diversity into animal production systems can increase their performance and strengthen their resilience. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 4: 109, ISSN: 2571-581X. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2020.00109.
El-Ashram, S.A., Aboelhadid, S.M., Abdel-Kafy, E.S.M., Hashem, S.A., Mahrous, L.N., Farghly, E.M. & Kamel, A.A. 2019. Prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of prebiotic supplementation against intestinal coccidiosis in rabbits. Animals, 9(11): 965, ISSN: 2076-2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9110965.
El-Deep, M.H., Amber, K.A., Elgendy, S., Dawood, M.A., Elwakeel, E.M. & Paray, B.A. 2020. Oxidative stress, hemato-immunological, and intestinal morphometry changes induced by ochratoxin A in APRI rabbits and the protective role of probiotics. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27: 35439-35448, ISSN: 0944-1344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09837-3.
Elmowalid, G.A.E., Ahmad, A.A.M., El-Hamid, M.I.A., Ibrahim, D., Wahdan, A., El Oksh, A.S. & Elnahriry, S.S. 2022. Nigella sativa extract potentially inhibited methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus induced infection in rabbits: potential immunomodulatory and growth promoting properties. Animals, 12(19): 2635, ISSN: 2076-2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192635.
El-Sabrout, K., Khalifah, A. & Ciani, F. 2023. Current applications and trends in rabbit nutraceuticals. Agriculture, 13(7): 1424, ISSN: 2077-0472. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13071424.
Fang, S., Chen, X., Ye, X., Zhou, L., Xue, S. & Gan, Q. 2020. Effects of gut microbiome and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) on finishing weight of meat rabbits. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11: 1835, ISSN: 1664-302X. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01835.
FAO/WHO. 2006. Probiotics in food: Health and nutritional properties and guidelines for evaluation. Roma, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, World Health Organization, Rome, Italy.
Florido, G.M., Laurencio, M., Rondón, A.J., Pérez, M., Arteaga, F., Bocourt, R. & Beruvides, A. 2017. Methodology for the isolation, identification and selection of Bacillus spp. strains for the preparation of animal additives. Cuban Journal of Agricultural Science, 51(2): 197-207, ISSN: 2079-3480. https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/1930/193057228005.pdf.
Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F., Ishaq, S.L., Rodriguez-Herrera, M.V., Garcia-Hernandez, C.A., Kawas, J.R. & Nagaraja, T.G. 2020. Are there indigenous Saccharomyces in the digestive tract of livestock animal species? Implications for health, nutrition and productivity traits. Animal, 14(1): 22-30, ISSN: 1751-732X. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731119001599.
Glajzner, P., Szewczyk, E.M., & Szemraj, M. 2023. Pathogenic potential and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolated from human and animals. Folia microbiologica, 68(2): 231-243, ISSN: 1874-9356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-022-01007-x.
Haj-Ayed, M. & Ben-Saïd, B. 2008. Effect of Tiamulin or Rescue-kit (R) on diet utilisation, growth and carcass yield of growing rabbits. World Rabbit Science, 16(3): 183-188, ISSN: 1989-8886. https://doi.org/10.4995/wrs.2008.627.
Hashem, N.M., El-Desoky, N., Hosny, N.S. & Shehata, M.G. 2020. Gastrointestinal microflora homeostasis, immunity and growth performance of rabbits supplemented with innovative non-encapsulated or encapsulated synbiotic. Proceedings, 73: 5, ISSN: 2504-3900. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECA2020-08894.
Ingweye, J.N., Anaele, O. & Ologbose, F.I. 2020. Response of rabbit bucks to diets containing Aidan (Tetrapleura tetraptera) as feed additive. Animal Research International, 17(2): 3691-3705, ISSN: 1597-3115. https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ari/article/view/199329.
Iser, M., Martínez, Y., Valdivié, M., Chipres, D.S. & Cortés, M.R. 2016. Comportamiento productivo y características de la canal de conejos alimentados con harina de Agave tequilana. REDVET. Revista Electrónica de Veterinaria, 17(10): 1-12, ISSN: 1695-7504. https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/636/63647454008.pdf.
Iser, M., Valdivié, M., Sánchez, D., Rosales, M., Más, D. & Martínez, Y. 2019. Effect of diet supplementation with meal of Agave tequilana stems on hematological indicators and blood biochemistry of fattening rabbits. Cuban Journal of Agricultural Science, 53(4): 403-412, ISSN: 2079-3480. https://cjascience.com/index.php/CJAS/article/view/920.
Johnson, N.C., Ogbamgba, V.M. & Mbachiantim, J.T. 2022. Growth Responses of Weaner Rabbits to Dietary Ginger (Zinger officinale) and Garlic (Allium sativum). European Journal of Science, Innovation and Technology, 2(1): 13-16, ISSN: 2786-4936. https://ejsit-journal.com/index.php/ejsit/article/view/59.
Kadja, L., Dib, A.L., Lakhdara, N., Bouaziz, A., Espigares, E. & Gagaoua, M. 2021. Influence of three probiotics strains, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 and Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 on the biochemical and Haematological profiles and body weight of healthy rabbits. Biology, 10(11): 1194, ISSN: 2079-7737. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111194.
Khan, K., Aziz, K., Khan, N.A., Khan, S. & Ayasan, T. 2021. Effect of enzyme and yeast-based feed additives on growth, nutrient digestibility, meat quality and intestinal morphology of fattening rabbits. Journal of the Hellenic Veterinary Medical Society, 72(4): 3511-3518, ISSN: 2585-3724. https://doi.org/10.12681/jhvms.29404.
Klassen, L., Reintjes, G., Li, M., Jin, L., Amundsen, C., Xing, X. & Abbott, D.W. 2023. Fluorescence activated cell sorting and fermentation analysis to study rumen microbiome responses to administered live microbials and yeast cell wall derived prebiotics. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13: 1020250, ISSN: 1664-302X. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.1020250.
Krysiak, K., Konkol, D. & Korczyński, M. 2021. Overview of the use of probiotics in poultry production. Animals, 11(6), ISSN: 2076-2615. https://doi.org/1620.10.3390/ani11061620.
Lebeque-Pérez, Y., Fong-Lores, O., Rodríguez-Leblanch, E., Llauradó-Maury, G. & Serrat-Díaz, M.J. 2022. Evaluación in vivo de la pirogenicidad de bioproductos fúngicos con potencial prebiótico. Revista Información Científica, 101(3), ISSN: 1028-9933. http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?pid=S1028-99332022000300008&script=sci_arttext.
Lee, N.K., Kim, W.S. & Paik, H.D. 2019. Bacillus strains as human probiotics: characterization, safety, microbiome, and probiotic carrier. Food Science and Biotechnology, 28: 1297-1305, ISSN: 2092-6456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00691-9.
Liu, L., Zuo, W. & Li, F. 2019. Dietary addition of Artemisia argyi reduces diarrhea and modulates the gut immune function without affecting growth performances of rabbits after weaning. Journal of Animal Science, 97(4): 1693-1700, ISSN: 1525-3163. https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/skz047.
Mali, S., Rathod, S., Kale, N. & Shinde, N. 2022. Overview of nutraceuticals. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 12(1): 61-70, ISSN: 2231-5691. https://doi.org/10.52711/2231-5691.2022.00010.
Mancini, S. & Paci, G. 2021. Probiotics in rabbit farming: Growth performance, health status, and meat quality. Animals, 11(12): 3388, ISSN: 2076-2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123388.
Martínez, Y., Iser, M., Valdivié, M., Galindo, J. & Sánchez, D. 2021. Supplementation with Agave fourcroydes powder on growth performance, carcass traits, organ weights, gut morphometry, and blood biochemistry in broiler rabbits. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Pecuarias, 12(3): 756-772, ISSN: 2448-6698. https://doi.org/10.22319/rmcp.v12i3.5892.
Martínez, Y., Iser, M., Valdivié, M., Rosales, M., Albarrán, E., & Sánchez, D. 2022. Dietary supplementation with Agave tequilana (weber var. Blue) stem powder improves the performance and intestinal integrity of broiler rabbits. Animals, 12(9): 1117, ISSN: 2076-2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12091117.
Morris-Quevedo, H. J., Llauradó-Maury, G., Bermúdez-Savón, R. C., Cos, P., Lebeque-Pérez, Y., Beltrán-Delgado, Y. & Gaime-Perraud, I. 2018. Evaluation of the immunomodulatory activity of bioproducts obtained from the edible-medicinal mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus. Biotecnología Aplicada, 35(3): 3511-3514, ISSN: 1027-2852. https://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/biotecapl/ba-2018/ba183e.pdf.
Nwachukwu, C.U., Aliyu, K.I. & Ewuola, E.O. 2021. Growth indices, intestinal histomorphology, and blood profile of rabbits fed probiotics-and prebiotics-supplemented diets. Translational Animal Science, 5(3): txab096, ISSN: 2573-2102. https://doi.org/10.1093/tas/txab096.
Olorunsogbon, B.F., Sangosina, M.I. & Olorunsogbon, A.M. 2022. Effect of orally administered aqueous extract of ginger and almond fruit extract on haematological and biochemical indices of weaned rabbits. Nigerian Journal of Animal Production, 49(2): 123-129, ISSN: 1596-5570. https://doi.org/10.51791/njap.v49i2.3469.
Oso, A.O., Idowu, O.M.O., Haastrup, A.S., Ajibade, A.J., Olowonefa, K.O., Aluko, A.O. & Bamgbose, A.M. 2013. Growth performance, apparent nutrient digestibility, caecal fermentation, ileal morphology and caecal microflora of growing rabbits fed diets containing probiotics and prebiotics. Livestock Science, 157(1): 184-190, ISSN: 1878-0490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2013.06.017.
Peralta-García, I., González-Muñoz, F., Elena, R.A.M., Sánchez-Flores, A. & López Munguía, A. 2020. Evolution of fructans in aguamiel (Agave sap) during the plant production lifetime. Frontiers in Nutrition, 7: 566950, ISSN: 2296-861X. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.566950.
Pogány-Simonová, M., Chrastinová, Ľ. & Lauková, A. 2020. Autochtonous strain Enterococcus faecium EF2019 (CCM7420), its bacteriocin and their beneficial effects in broiler rabbits—A review. Animals, 10(7): 1188, ISSN: 2076-2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10071188.
Santurio, J.M., Alves, S.H., Pereira, D.I.B., Vetvicka, V. & Oliveira, C. 2020. Effect of yeast purified β-glucan in experimental treatment of pythiosis in rabbits. International Clinical Pathology Journal, 8: 14-20, ISSN: 2471-0016. https://doi.org/10.15406/icpjl.2020.08.00199.
Suárez-Machín, C., Mora-Castellanos, L.M., Savón-Valdés, L.L., Carrera-Bocourt, E. & Díaz-de Villegas, M.E. 2022. Caracterización físico-química y microbiológica del Lebame para su uso como probiótico en la alimentación de conejos, en crecimiento-ceba. Revista ICIDCA, 56:1, ISSN: 2410-8529. https://www.revista.icidca.azcuba.cu/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/articulo-3-1.pdf.
Sun, H., Ni, X., Song, X., Wen, B., Zhou, Y., Zou, F. & Wang, P. 2016. Fermented Yupingfeng polysaccharides enhance immunity by improving the foregut microflora and intestinal barrier in weaning rex rabbits. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,100: 8105-8120, ISSN: 1432-0614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7619-0.
Treiber, F.M. &Beranek-Knauer, H. 2021. Antimicrobial residues in food from animal origin—A review of the literature focusing on products collected in stores and markets worldwide. Antibiotics, 10(5): 534, ISSN: 2079-6382. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050534.
Vidovic, N. & Vidovic, S. 2020. Antimicrobial resistance and food animals: Influence of livestock environment on the emergence and dissemination of antimicrobial resistance. Antibiotics, 9(2): 52, ISSN: 2079-6382. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020052.
Wlazło, Ł., Kowalska, D., Bielański, P., Chmielowiec-Korzeniowska, A., Ossowski, M., Łukaszewicz, M. & Nowakowicz-Dębek, B. 2021. Effect of fermented rapeseed meal on the gastrointestinal microbiota and immune status of rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus).Animals, 11(3): 716, ISSN: 2076-2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030716.
Xie, H., Yu, E., Wen, H., Jiang, B., Fu, G., Sun, H. & He, J. 2022. Effects of dietary daidzein supplementation on reproductive performance, immunity, and antioxidative capacity of New Zealand White does.Animal Feed Science and Technology, 292: 115431, ISSN: 1873-2216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2022.115431.
Xie, H., Yu, E., Wen, H., Jiang, B., Fu, G., Sun, H. & He, J. 2023. Maternal Daidzein Supplementation during Lactation Promotes Growth Performance, Immunity, and Intestinal Health in Neonatal Rabbits.Agriculture, 13(9): 1654, ISSN: 2077-0472. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13091654.
Zemzmi, J., Ródenas, L., Blas, E., Abdouli, H., Najar, T., & Pascual, J.J. 2020. Preliminary evaluation of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) seed gum as a potential prebiotic for growing rabbits in Tunisia: effects on in vivo faecal digestibility and in vitro fermentation.World Rabbit Science, 28(3): 113-122, ISSN: 1989-8886. https://doi.org/10.4995/wrs.2020.12994.
Zhu, Y.T., Yue, S.M., Li, R.T., Qiu, S.X., Xu, Z.Y., Wu, Y. & Li, Y. 2021. Prebiotics inulin metabolism by lactic acid bacteria from young rabbits.Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 8: 719927, ISSN: 2297-1769. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2021.719927.